IP Fundamental
Table of contents
IP - layer 3
- IPv4 uses
32-bit addresses
4 x 8 bits = 32 (4 x octet, 1 octet = 8 bits)
aaaaaaaa bbbbbbbb cccccccc dddddddd -> xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
inet -> ipv4
inet6 -> ipv6
Binary to Decimal
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 = 183
128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 183
-----> * count start right (small number) to left (large number)
1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 = 183
128 + 0 + 32 + 16 + 0 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 183
- ipv4 availability = 2 ^ 32 = 4,294,967,296 (4 billion)
- ipv6 availability = 2 ^ 128 = xxxxxx
Private IP address
CIDR notation - subnetting
- CIDR: Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- Understand Mbps (megabits for speed) vs MBps (megabytes for data)
- Most common: 255.255.255.0 = /24, 256 hosts available for this.
Example IP: 192.168.2.64/26
`/26` is subnet mask
/26 -> 26 x 1 -> 11111111 11111111 1111111 11 000000 (subnet mask)
-------- -------- -------- -- ------
192 168 2 64
11000000 10101000 00000010 01 000000 (ip address)
-------- -------- -------- -- ------
fixed fixed fixed | 000000 (lowest) -> network address
| any number in between -> host ID
fixed fixed fixed | 111111 (highest) -> broadcast address
conclusion:
11000000 10101000 00000010 01000000 -> 192.168.2.64 -> network ID
11000000 10101000 00000010 01111111 -> 192.168.2.127 -> broadcast ID
192.168.2.64 -> xxx.xxx.x.65 ... -> 126 are the host ID
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| subnet | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | pervious x 2
| host | 256 | 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | pervious / 2
| subnet mask | /24 | /25 | /26 | /27 | /28 | /29 | /30 | /31 | /32 |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Network Host
-----------------------------------
| 192 . 168 . 32 | . 152 |
| 255 . 255 . 255 | . 0 |
-----------------------------------
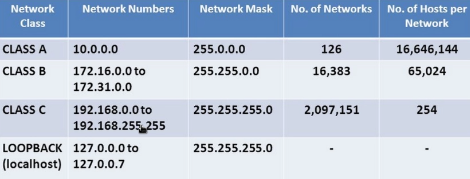
| Class | | Subnet | Total available hosts |
| A | 1.0.0.0 - 126.255.255.255 | 255.0.0.0 | 16,777,214 |
| B | 128.0.0.0 - 191.255.255.255 | 255.255.0.0 | 65,534 |
| C | 192.0.0.0 - 223.255.255.255 | 255.255.255.0 | 254 |
| D & E | E is reserved | | |
- Public ip: unique, one ip per household
- Private ip: reusable range from
192.168.0.1 to 192.168.0.255, for printer, phone, ip per device.
MAC address (layer 2, relating to switch)
ether = mac address: 82:bf:72:63:40:05 (use mac address lookup, virgin media)
--------
first 3 pairs is `identifier`
TCP, UDP, and the 3-way handshake (layer 4)
- SYN > SYN ACK > ACK
- 65,000 + ports available
Common ports and protocols:
| TCP | UDP |
| ftp 21 | dns 53 |
| ssh 22 | dhcp 67, 68 |
| telnet 23 | tftp 69 |
| smtp 25 | snmp 161 |
| dns 53 | |
| pop3 110 | |
| smb 139 + 445 | |
| imap 143 | |
OSI model
Layers - Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away
- Physical - data cables, cat 6 - please
- Data - switching, MAC addresses - do
- Network - IP addresses, routing - not
- Transport - TCP / UDP - throw
- Session - session management - sausage
- Presentation - WMV, JPEG, MOV - pizza
- Application - HTTP, SMTP - away
| Layer | TCP / IP Model | OSI model (7 layers) |
| L7 | Application layer | Presentation layer |
| | Session layer | |
| L4 | Transport layer | Transport layer / UDP header / tcp header |
| L3 | Internet Layer | network layer / ip protocol layer / IP header |
| L2 | network access layer | Data Link Layer |
| | physical layer | |
